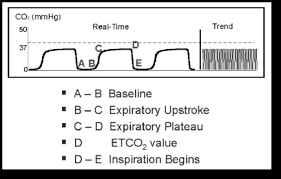
end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr. The initial values of PetCO2 were significantly higher in the group with asphyxial cardiac arrest 674 422 kilopascals kPa versus 451 247 kPa.

End Tidal Co2 Monitoring Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring For The
Increasing CO2 during CPR can also indicate the return of spontaneous circulation.

. In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa was associated with an almost five-fold higher rate of return. End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end.
EtCO2 represents the amount of carbon dioxide at the end of exhalation. Predicting likelihood of return of. CO2 will decrease prior to a cardiac arrest in patients that are intubated in an intensive care setting.
Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS.
More Than Just a Number. Geoff Murphy from Master Your Medics provides a refresher training video on end. Immediate causes of arrests were hypotension in 74 respiratory decompensation in 28 and arrhythmia in 14.
Increasing CO2 during CPR can also indicate the return of spontaneous circulation. The use of capnography to guide the length of resuscitation efforts is an exciting area for future research. A spike in ETCO2 reading is the first sign of ROSC and a drop in.
The Journal of Emergency Medicine released an article traumatic brain injury careOriginal Article. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a. End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation.
In the group with asphyxial cardiac arrest the initial values of PetCO2 did not show a significant difference when we. During CPR median ETCO2 was 23 mmHg median ventilation rate was 29. End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiac Arrest.
End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field. Feb 6 2019.
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

End Tidal Co2 In Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Etco2 In Cpr

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Pdf Difference In End Tidal Co2 Between Asphyxia Cardiac Arrest And Ventricular Fibrillation Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiac Arrest In The Prehospital Setting
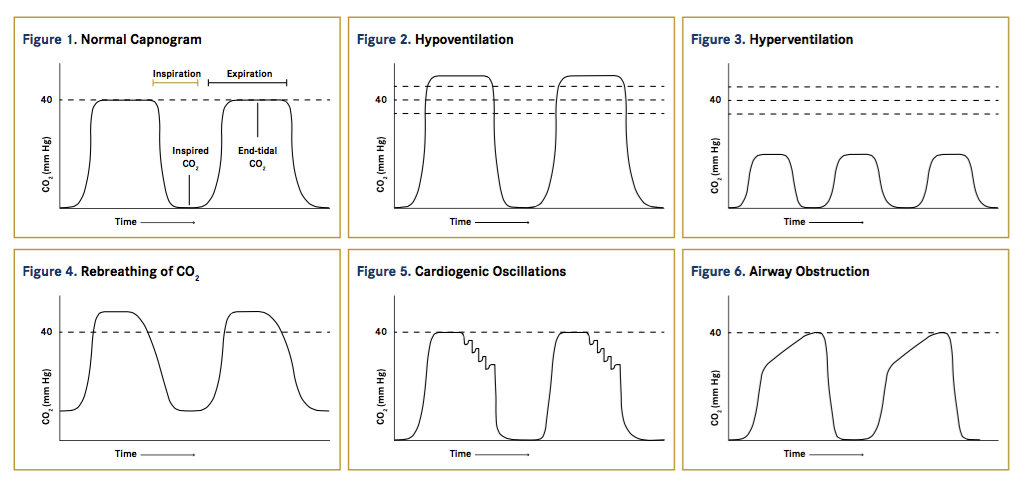
Avma 2017 Anesthesia Monitoring With Capnography

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions Kodali Bs Urman Rd J Emerg Trauma Shock

Capnography During Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Abstract 223 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels Predict Cardiac Arrest Circulation

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Rogue Capno Waves Resuscitation Team Notes Unusual Waveform During Cpr Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
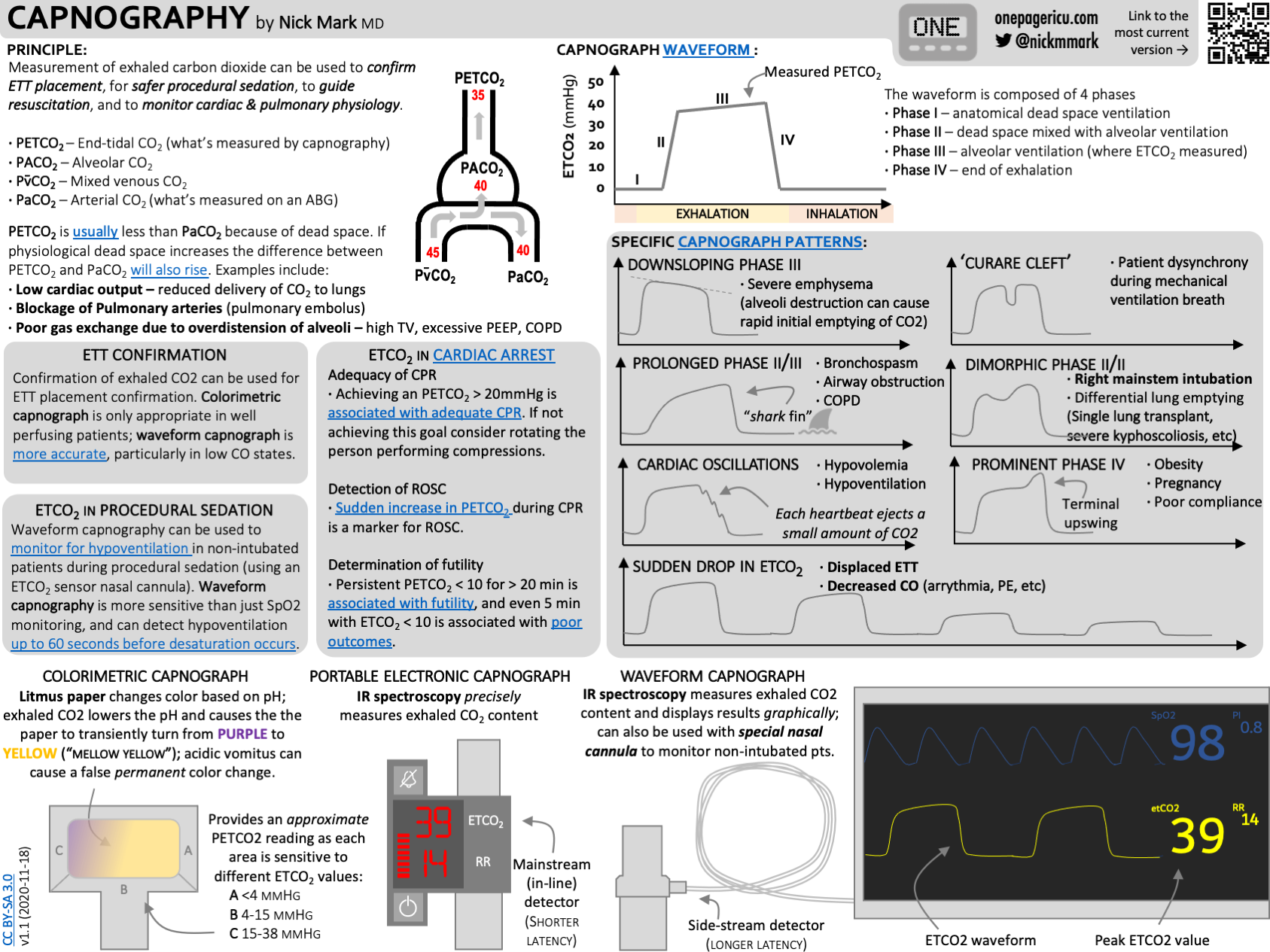
Capnography Etco2 Icu One Pager

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Nejm

The Prognostic Value Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide During Cardiac Arrest A Systematic Review Resuscitation